The genetic male sterile referred to as msg,,bk originated as a spontaneous mutant isolated by Eslick and Ramage from the cultivar 'Betzes' as B67N-89 (Hockett, 1972). Hockett (1972) reported that msg,,bk is a simply inherited recessive gene which produces plants with nearly normal anthers and about 1% self-fertility. Eslick et al. (1974) assigned msg,,bk to chromosome 6 based on results a primary trisomic analysis. Linkage between msg,,bk and o (orange lemma) and 9~4 (glossy sheath 4) was demonstrated also. Ramage and Paluska (1975) provided evidence that msg,,bk is located on the short arm of chromosome 6.
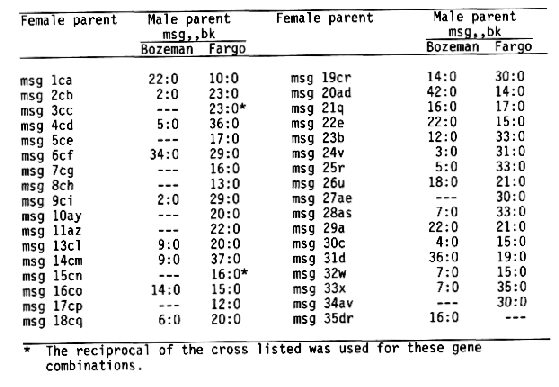
Progeny from crosses between msg,,bk heterozygotes and lines homozygous for numbered male sterile genes demonstrated that msg,,bk is not allelic to msg1 through msg35 (Table 1). The multiple recessive marker stock for chromosome 6 developed by R.I. Wolfe was used in most crosses at Fargo as the male parent heterozygous at the msg,,bk locus. The gene symbol msg36bk is suggested for the msg,,bk gene.
References:
Eslick, R.F., R.T. Ramage, and D.R. Clark. 1974. Two genetic male steriles, msg 6 and msg,,bk, assigned to chromosome 6. Barley Genet. Newsl. 4:11-15.
Hockett, E.A. 1972. Coordinator's report on the genetic male sterile barley collection. Barley Genet. Newsl. 2:139-144.
Hockett, E.A. 1979. The genetic male sterile barley collection. Barley Genet. Newsl. 9:124-128.
Ramage, R.T., and M. Paluska. 1975. Mapping chromosome 6. Barley Genet. Newsl. 5:49-51.