

Vol. Plant Chitinases are potent inhibitors of fungal growth which are integrated in a complex biochemical defense system (Schlumbaum et al., 1986). A previously characterized barley grain protein C (Hejgaard and Bjorn 1985) was found to possess chitinase activity. The N-terminal sequence: S-V-S-S-I-V-S-R-A-Q-F-D-R-M-L-L-H-R-N- showed homology (53% of amino acids in identical positions) with sequences in endochitinases from bean leaves and cultured tobacco pith tissue (Broglie et al., 1986, Shinshi et al., 1987).
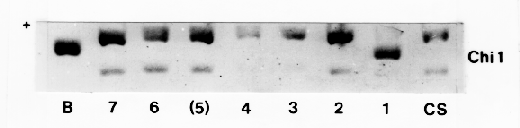
Chromosomal assignment was based on wheat - barley addition lines obtained from Dr. A. K. M. R. Islam, Adelaide. Proteins in water extracts were separated by cathodic starch gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose by electro-blotting. Immunochemical detection with monospecific antibodies showed that the locus encoding the grain chitinase is on barley chromosome 1 (7H). The locus designation (Chi 1) is suggested.
References:
Broglie, K. E., J. J. Gaynor and R. M. Broglie. 1986. Ethylene-regulated gene expression: Molecular cloning of the genes encoding an endochitinase from Phaseolus vulgaris. Proc. Natl. Acade. Sci. USA 83:6820-6824.
Hejgaard, J. and S. E. Bjorn. 1985. Four major basic proteins of barley grain. Purification and partial characterization. Physiol. Plant. 64:301-307.
Schlumbaum, A., F. Mauch, U. Vogli and T. Boller. 1986. Plant chitinases are potent inhibitors of fungal growth. Nature 324:365-367.
Shinshi, H., D. Mohnen and F. Meins. 1987. Regulation of plant pathogenesis-related enzyme: Inhibition of chitinase and chitinase mRNA accumulation in cultured tobacco tissues by auxin and cytokinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:89-93.